Me.UltraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Override.RowFilterAction = RowFilterAction.NoneThis topic demonstrates, with code examples, how to enable and implement external filtering functionality in the WinGrid™ control.
This topic contains the following sections:
With external filtering enabled, the UltraGrid™ control’s built-in filtering user interface (UI) is retained, but the internal filtering logic is bypassed and there is no need for all rows to be loaded at the same time. This enables WinGrid to filter data with the supplied custom filtering code and also utilize the LoadOnDemand functionality*.*
To enable external filtering, you need to disable the default filtering action and some events must be added to handle your custom filtering logic and populate the filter value list with your custom filtering values. (The filter value list will not be populated by the grid. However, the default options Custom, Blanks, NonBlanks , and All will be available in the filter drop-down.)
The following table lists the steps to enabling external filtering.
Set the RowFilterAction property to None .
In Visual Basic:
Me.UltraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Override.RowFilterAction = RowFilterAction.NoneIn C#:
this.ultraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Override.RowFilterAction = RowFilterAction.None;Handle the BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulate event.
In Visual Basic:
Private Sub UltraGrid1_BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulate(ByVal sender As System.Object, _
ByVal e As Infragistics.Win.UltraWinGrid.BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulateEventArgs) Handles UltraGrid1.BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulate
End SubIn C#:
private void ultraGrid1_BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulate(object sender, BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulateEventArgs e)
{
}Handle the AfterRowFilterChanged event.
In Visual Basic:
Private Sub UltraGrid1_AfterRowFilterChanged(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As Infragistics.Win.UltraWinGrid.AfterRowFilterChangedEventArgs) Handles UltraGrid1.AfterRowFilterChanged
End SubIn C#:
private void ultraGrid1_AfterRowFilterChanged(object sender, AfterRowFilterChangedEventArgs e)
{
}The following example demonstrates how to implement custom filtering to display and filter values starting with A, B, C, D from the Text column of the WinGrid. This is achieved by adding custom filtering logic to display the alphabets A, B, C, and D in the filter drop-down of the Text column and filtering the grid by the selected value from the filter drop-down list.
In this example, the WinGrid control is bound to the WinDataSource™ component. For the purpose of demonstration, a dataset is used as the back-end data storage which supplies data for the WinDataSource™ component.
The following screenshot is a preview of the final result: WinGrid showing records filtered out using the custom filtering logic with in-built filtering UI.
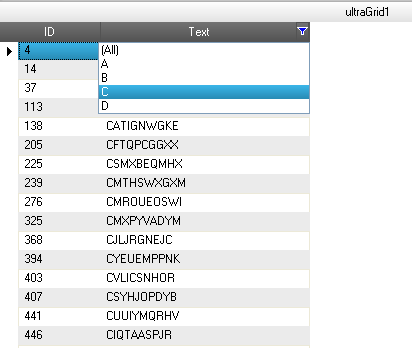
To complete the procedure, you need the following:
A form with an UltraGrid control and UltraDataSource component added to it
Following is a conceptual overview of the process:
Defining private members
Configuring the back-end data storage
Generating random data
Defining the row/column schema for the data source component
Defining the grid load style
Disabling the default filtering action
Supplying the data
Populating the drop-down with the custom filtering values
Adding your custom filtering logic
The following steps demonstrate how to enable external filtering on WinGrid and apply the custom filtering logic stated in the Introduction.
Define a dataset and data row.
In Visual Basic:
Imports Infragistics.Win
Imports Infragistics.Win.UltraWinGrid
Private ds As DataSet
Private rows As DataRow()In C#:
using Infragistics.Win;
using Infragistics.Win.UltraWinGrid;
private DataSet ds;
private DataRow[] rows;A dataset with two columns and one million rows is defined.
In Visual Basic:
Dim dt As New DataTable()
Dim dc As New DataColumn("ID")
dc.DataType = System.Type.[GetType]("System.Int32")
dt.Columns.Add(dc)
dc = New DataColumn("Text")
dc.DataType = System.Type.[GetType]("System.String")
dt.Columns.Add(dc)
Dim dr As DataRow
For i As Integer = 0 To 999999
Dim record As New Record(Me.GetRandomString(10))
dr = dt.NewRow()
dr(0) = record.id
dr(1) = record.textField
dt.Rows.Add(dr)
Next
ds = New DataSet()
ds.Tables.Add(dt)
rows = dt.[Select]()In C#:
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
DataColumn dc = new DataColumn("ID");
dc.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.Int32");
dt.Columns.Add(dc);
dc = new DataColumn("Text");
dc.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.String");
dt.Columns.Add(dc);
DataRow dr;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
Record record = new Record(this.GetRandomString(10));
dr = dt.NewRow();
dr[0] = record.id;
dr[1] = record.textField;
dt.Rows.Add(dr);
}
ds = new DataSet();
ds.Tables.Add(dt);
rows = dt.Select();The following code generates random data, which is supplied to the UltraDataSource component within the CellDataRequested event. Random strings are supplied to the Text column.
In Visual Basic:
Private Class Record
Friend Shared ID_COUNTER As Integer = 0
Friend id As Integer
Friend textField As String
Friend Sub New(ByVal textField As String)
Me.id = ID_COUNTER
ID_COUNTER += 1
Me.textField = textField
End Sub
End Class
Private random As New Random()
Private Function GetRandomString(ByVal len As Integer) As String
Dim sb As System.Text.StringBuilder = New System.Text.StringBuilder(len)
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To len - 1
Dim a As Char = "A"
Dim z As Char = "Z"
sb.Append(Chr(Asc(a) + Me.random.Next(Asc(z) - Asc(a))))
Next
Return sb.ToString()
End FunctionIn C#:
private class Record
{
internal static int ID_COUNTER = 0;
internal int id;
internal string textField;
internal Record(string textField)
{
this.id = ID_COUNTER;
ID_COUNTER++;
this.textField = textField;
}
}
private Random random = new Random();
private string GetRandomString(int len)
{
System.Text.StringBuilder sb = new System.Text.StringBuilder(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
sb.Append((char)('A' + this.random.Next('Z' - 'A')));
return sb.ToString();
}Add this code within Form load event to define the columns and rows for the UltraDataSource™ component.
In Visual Basic:
' Add two columns, one ID column of type int and second Text column of
' type string.
Me.UltraDataSource1.Band.Columns.Add("ID", GetType(Integer))
' Make id column read-only.
Me.UltraDataSource1.Band.Columns("ID").[ReadOnly] = DefaultableBoolean.[True]
Me.UltraDataSource1.Band.Columns.Add("Text", GetType(String))
' Set the row count. This is how many rows we will have.
Me.UltraDataSource1.Rows.SetCount(Me.ds.Tables(0).Rows.Count)In C#:
// Add two columns, one ID column of type int and second Text column of type string.
this.ultraDataSource1.Band.Columns.Add("ID", typeof(int));
// Make id column read-only.
this.ultraDataSource1.Band.Columns["ID"].ReadOnly = DefaultableBoolean.True;
this.ultraDataSource1.Band.Columns.Add("Text", typeof(string));
// Set the row count. This is how many rows we will have.
this.ultraDataSource1.Rows.SetCount(this.ds.Tables[0].Rows.Count);Set LoadStyle to LoadOnDemand so that the grid can load data on demand. Add this code within the form’s Load event.
In Visual Basic:
' Set the LoadStyle to LoadOnDemand so the UltraGrid 'doesn't pre-load all the rows. LoadOnDemand load style 'creates rows as they are needed (for example when they are 'scrolled into view). You must do this before setting the 'DataSource on the UltraGrid.
Me.UltraGrid1.DisplayLayout.LoadStyle = LoadStyle.LoadOnDemandIn C#:
// Set the LoadStyle to LoadOnDemand so the UltraGrid //doesn't pre-load all the rows. LoadOnDemand load style //creates rows as they are needed (for example when they //are scrolled into view). You must do this before setting //the DataSource on the UltraGrid.
this.ultraGrid1.DisplayLayout.LoadStyle = LoadStyle.LoadOnDemand;In order to display the WinGrid control’s built-in filtering UI without any internal filtering logic, the RowFilterAction property must be set to None. Since internal filtering logic is bypassed, the grid data can load data on demand.
Add this code within the form’s load event.
In Visual Basic:
Me.UltraGrid1.DataSource = Me.UltraDataSource1
Me.UltraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Bands(0).Columns("Text").AllowRowFiltering = DefaultableBoolean.[True]
' Enable only the Filtering UI of UltraGrid without any filtering action
Me.UltraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Override.RowFilterAction = RowFilterAction.NoneIn C#:
this.ultraGrid1.DataSource = this.ultraDataSource1;
this.ultraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Bands[0].Columns["Text"].AllowRowFiltering = DefaultableBoolean.True;
// Enable only the Filtering UI of UltraGrid without any filtering action
this.ultraGrid1.DisplayLayout.Override.RowFilterAction = RowFilterAction.None;The data required for the UltraDataSource component is supplied from within the CellDataRequested event. This event is fired when an UltraGrid bound to UltraDataSource component, requests value for a cell and the UltraDataSource component doesn’t have the cell values. The following code resides within the CellDataRequested event of the UltraDataSource component.
In Visual Basic:
Dim columnKey As String = e.Column.Key
If rows.Length > e.Row.Index Then
If "ID" = columnKey Then
e.Data = CInt(rows(e.Row.Index)(0))
ElseIf "Text" = columnKey Then
e.Data = DirectCast(rows(e.Row.Index)(1), String)
End If
End If
' By default UltraDataSource will cache the provided cell value and not ask for
' it next time it's needed. Set CacheData to false to prevent UltraDataSource
' from doing so.
e.CacheData = FalseIn C#:
string columnKey = e.Column.Key;
if (rows.Length > e.Row.Index)
{
if ("ID" == columnKey)
{
e.Data = (int)rows[e.Row.Index][0];
}
else if ("Text" == columnKey)
{
e.Data = (string)rows[e.Row.Index][1];
}
}
// By default UltraDataSource will cache the provided cell value and not ask for
// it next time it's needed. Set CacheData to false to prevent UltraDataSource
// from doing so.
e.CacheData = false;The BeforeRowFilterDropDownPopulate event of the UltraGrid must be handled to manually populate the filter drop-down value list items. Here the filter drop down is populated with the alphabets ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ and ‘D’ as the value list items.
In Visual Basic:
' Add code to manually populate the filter drop down here...
If "Text" = e.Column.Key Then
' The following code demonstrates removing of default value list items from the filter drop down
For i As Integer = e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Count - 1 To 0 Step -1
' Remove 'Custom' option from the filter drop down.
If e.ValueList.ValueListItems(i).DisplayText.Equals("(Custom)") Then
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i)
' Remove 'Blanks' option from the filter drop down.
ElseIf e.ValueList.ValueListItems(i).DisplayText.Equals("(Blanks)") Then
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i)
' Remove 'NonBlanks' option from the filter drop down.
ElseIf e.ValueList.ValueListItems(i).DisplayText.Equals("(NonBlanks)") Then
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i)
End If
Next
' Populate the filter drop-down with four items that filter by 'the first letter of the cell value.
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("A")
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("B")
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("C")
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("D")
End IfIn C#:
// Add code to manually populate the filter drop down here...
if ("Text" == e.Column.Key)
{
// The following code demonstrates removing of default value list items from the filter drop down
for (int i = e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
// Remove 'Custom' option from the filter drop down.
if (e.ValueList.ValueListItems[i].DisplayText.Equals("(Custom)"))
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i);
// Remove 'Blanks' option from the filter drop down.
else if (e.ValueList.ValueListItems[i].DisplayText.Equals("(Blanks)"))
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i);
// Remove 'NonBlanks' option from the filter drop down.
else if (e.ValueList.ValueListItems[i].DisplayText.Equals("(NonBlanks)"))
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.RemoveAt(i);
}
// Populate the filter drop-down with four items that filter by // the first letter of the cell value.
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("A");
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("B");
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("C");
e.ValueList.ValueListItems.Add("D");To add custom filtering logic, the AfterRowFilterChanged event of the UltraGrid must be handled. Here, the code is written to filter all the records starting with the alphabet that is selected from the Text column filter drop-down list.
In Visual Basic:
If e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions.Count > 0 Then
' Set the cursor to wait since it might take a while for the filter operation to complete.
Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor
If (e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions(0).CompareValue).ToString() = "A" Then
rows = ds.Tables(0).[Select]("Text LIKE 'A%'")
ElseIf (e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions(0).CompareValue).ToString() = "B" Then
rows = ds.Tables(0).[Select]("Text LIKE 'B%'")
ElseIf (e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions(0).CompareValue).ToString() = "C" Then
rows = ds.Tables(0).[Select]("Text LIKE 'C%'")
ElseIf (e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions(0).CompareValue).ToString() = "D" Then
rows = ds.Tables(0).[Select]("Text LIKE 'D%'")
End If
Else
rows = ds.Tables(0).[Select]()
End If
Cursor.Current = Cursors.[Default]
' Clears all cached cell values
Me.UltraDataSource1.Rows.ResetCachedValues()
Me.UltraDataSource1.Rows.SetCount(rows.Length)In C#:
if (e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions.Count > 0)
{
// Set the cursor to wait since it might take a while for the filter operation to complete.
Cursor.Current = Cursors.WaitCursor;
if ((e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions[0].CompareValue).ToString() == "A")
{
rows = ds.Tables[0].Select("Text LIKE 'A%'");
}
else if ((e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions[0].CompareValue).ToString() == "B")
{
rows = ds.Tables[0].Select("Text LIKE 'B%'");
}
else if ((e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions[0].CompareValue).ToString() == "C")
{
rows = ds.Tables[0].Select("Text LIKE 'C%'");
}
else if ((e.NewColumnFilter.FilterConditions[0].CompareValue).ToString() == "D")
{
rows = ds.Tables[0].Select("Text LIKE 'D%'");
}
}
else
{
rows = ds.Tables[0].Select();
}
Cursor.Current = Cursors.Default;
// Clears all cached cell values
this.ultraDataSource1.Rows.ResetCachedValues();
this.ultraDataSource1.Rows.SetCount(rows.Length);To verify the result, click the filter icon on the Text column of the Grid. If external filtering is implemented correctly, the filter criteria should be visible and functional in the drop-down as shown in the Preview.
The following topics provide additional information related to this topic.