This topic provides information on how triangulation of data points works as well as how it can improve the performance of rendering data in the XamGeographicMap™ control.
The following table lists the topics required as a prerequisite to understanding this topic.
This topic contains the following sections
Triangulation is a process of triangulating data points with the same values based on their longitude and latitude locations. Consider the following simplified scenario of triangulating data in a geographic context:
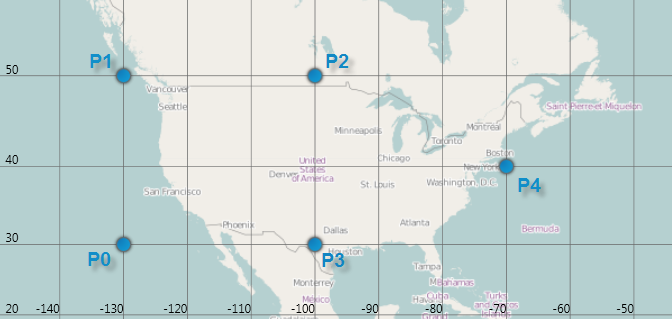
The following is a screenshot of (-130, 30), (-130, 50), (-100, 50), (-100, 30), (-70, 40) geographic locations plotted using the GeographicScatterAreaSeries.

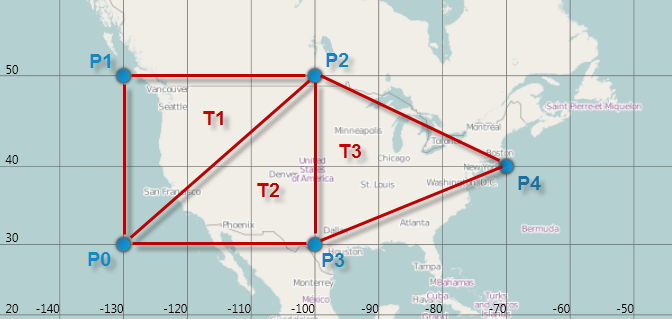
For the above five points, there are three triangles and their triangle vertex indices are as follows: (0, 1, 2), (0, 2, 3), (2, 3, 4).
The following image shows these triangles and their vertex indices.
In the XamGeographicMap control, the TriangulationSource class represents the data source for creating, loading, and saving triangulation. A complete data structure for TriangulationSource consist of two properties that are listed in the following table:
The TriangulationSourcePointRecord class represents one of the triangle points in triangulation. The following table lists key properties of the TriangulationSourcePointRecord class.
The Triangle class represents a record with three integer values or triangle vertex indices. Each integer is an index which corresponds to a point in the Points collection. The following table lists key properties of the Triangle class.
Triangulation data can also be stored in triangulation files that use the Intermediate Triangular Irregular Network Format (or ITF for short). For more information on this file format and its specifications, please visit this website.
The TriangulationSource class provides methods for creating triangulation, saving and loading triangulation data to and from ITF files.
The following table lists key methods in the TriangulationSource class for working with triangulation data
In the XamGeographicMap control, the following types of geographic series can use pre-triangulated data or perform triangulation of data at runtime if no triangulation source is specified:
These types of series provide built-in data triangulation that is automatically performed on items in the ItemsSource if no triangulation is set to the TrianglesSource property. However, computing triangulation can be a very time-consuming process, so the runtime performance will be better when specifying a TriangulationSource for this property, especially when a large number of data items are present. Therefore, you should avoid this computation at run-time by “pre-triangulating” the data and providing the triangulation to a geographic series.
The following table list the main steps of pre-triangulation process:
After completing the pre-triangulation process, a step for binding a geographic series to triangulation data is necessary. Please refer to the following topics for a more detailed explanation. in:
The TriangulationSource class provides the Create method for creating triangulation of geographic data. This static method creates a TriangulationSource using delegates to get the Points and Triangles to create a triangulation.
The following code demonstrates how to create triangulation from shape files by implementing a handler for ImportCompleted event of the ShapefileConverter class and passing delegates to get Points and Fields collections to the Create method of the TriangulationSource class.
In Visual Basic:
Imports Infragistics.Controls.Charts
Imports Infragistics.Controls.Maps
Imports System.ComponentModel
Private WithEvents converter As New ShapefileConverter()
converter.ShapefileSource = New Uri("nws_precip_1day_observed_20110419.shp", System.UriKind.RelativeOrAbsolute)
converter.DatabaseSource = New Uri("nws_precip_1day_observed_20110419.dbf", System.UriKind.RelativeOrAbsolute)
Private Sub OnShapeFileConverterImportCompleted(sender As Object, e As AsyncCompletedEventArgs) Handles converter.ImportCompleted
Dim triangulationSource As TriangulationSource = TriangulationSource.Create(converter.Count,
Function(i) converter(i).Points(0)(0),
Function(i) Convert.ToSingle(converter(i).Fields("Globvalue")))
End SubIn C#:
using Infragistics.Controls.Charts;
using Infragistics.Controls.Maps;
using System.ComponentModel;
var converter = new ShapefileConverter();
converter.ImportCompleted += OnShapeFileConverterImportCompleted;
converter.ShapefileSource= new Uri("nws_precip_1day_observed_20110419.shp", System.UriKind.Relative);
converter.DatabaseSource = new Uri("nws_precip_1day_observed_20110419.dbf", System.UriKind.Relative);
void OnShapeFileConverterImportCompleted(object sender, AsyncCompletedEventArgs e)
{
TriangulationSource triangulationSource = TriangulationSource.Create(converter.Count,
(i) => converter[i].Points[0][0],
(i) => Convert.ToSingle(converter[i].Fields["Globvalue"]));
}The TriangulationSource class provides the SaveItf method for saving triangulation of geographic data. This static method saves a triangulation to binary ITF file that you can deploy with your application and use later for loading triangulation data.
The following code demonstrates how to save triangulation data to an ITF file by providing an IsolatedStorageFileStream to the SaveItf method of the TriangulationSource class.
In Visual Basic:
Using iso As IsolatedStorageFile = IsolatedStorageProvider.GetIsolatedStorageFile()
Dim filePath As String = "TriangulatedFile.itf"
Using stream = New IsolatedStorageFileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create, iso)
triangulationSource.SaveItf(stream)
stream.Close()
End Using
End UsingIn C#:
using (IsolatedStorageFile iso = IsolatedStorageProvider.GetIsolatedStorageFile())
{
string filePath = "TriangulatedFile.itf";
using (var stream = new IsolatedStorageFileStream(filePath, FileMode.Create, iso))
{
triangulationSource.SaveItf(stream);
stream.Close();
}
}Similar to saving triangulation method, the TriangulationSource class also provides the LoadItf method for loading triangulation of geographic data. This static method loads a triangulation data from binary ITF file.
The following code demonstrates how to load triangulation from an ITF file by providing an IsolatedStorageFileStream of an ITF file and passing it to the TriangulationSource class’ LoadItf method.
In Visual Basic:
Dim triangulationSource As TriangulationSource
Using iso As IsolatedStorageFile = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForAssembly()
Dim filePath As String = "TriangulatedFile.itf"
If iso.FileExists(filePath) Then
Using stream = New IsolatedStorageFileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, iso)
triangulationSource = TriangulationSource.LoadItf(stream)
stream.Close()
End Using
End If
End UsingIn C#:
TriangulationSource triangulationSource;
using (IsolatedStorageFile iso = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForAssembly();
{
string filePath = "TriangulatedFile.itf";
if (iso.FileExists(filePath))
{
using (var stream = new IsolatedStorageFileStream(filePath, FileMode.Open, iso))
{
triangulationSource = TriangulationSource.LoadItf(stream);
stream.Close();
}
}
}Using the ItfConverter method is an alternative for loading triangulation data from an ITF file as demonstrated in the following code:
In XAML:
<ig:ItfConverter x:Key="itfConverter"
Source="TriangulatedFile.itf" >
</ig:ItfConverter>In Visual Basic:
Dim itfConverter = New ItfConverter()
itfConverter.Source = New Uri("TriangulatedFile.itf", UriKind.RelativeOrAbsolute)
Dim triangulationSource As TriangulationSource = itfConverter.TriangulationSourceIn C#:
var itfConverter = new ItfConverter();
itfConverter.Source = new Uri("TriangulatedFile.itf", UriKind.RelativeOrAbsolute);
TriangulationSource triangulationSource = itfConverter.TriangulationSource;The following topics provide additional information related to this topic.