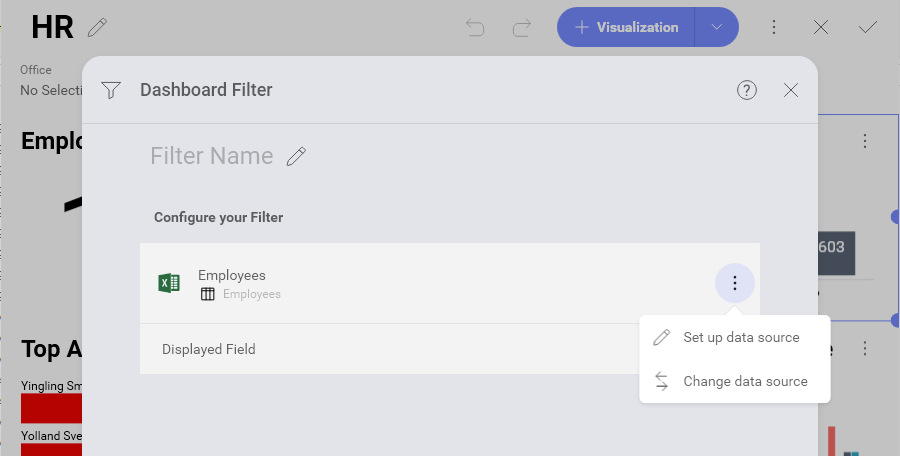
In order to add a new dashboard filter:
Go to the Dashboard editor and select Add Filter ⇒ Add Dashboard Filter.
The Dashboard Filter menu will open. By default, the selected data source will be the data source used in your first visualization. You can configure or change it using the overflow menu next to the data source’s name.

Choose which dataset to use as a dashboard filter and click/tap Select Data.
You will be able to change the following settings for the filter:
This setting specifies the dataset field that will be used to display the values in the Dashboard Filters. Listed values will not be repeated, even if they appear multiple times in the original dataset.
You can change the displayed column in Edit mode by selecting the Edit button in the overflow menu next to the dashboard filter name.
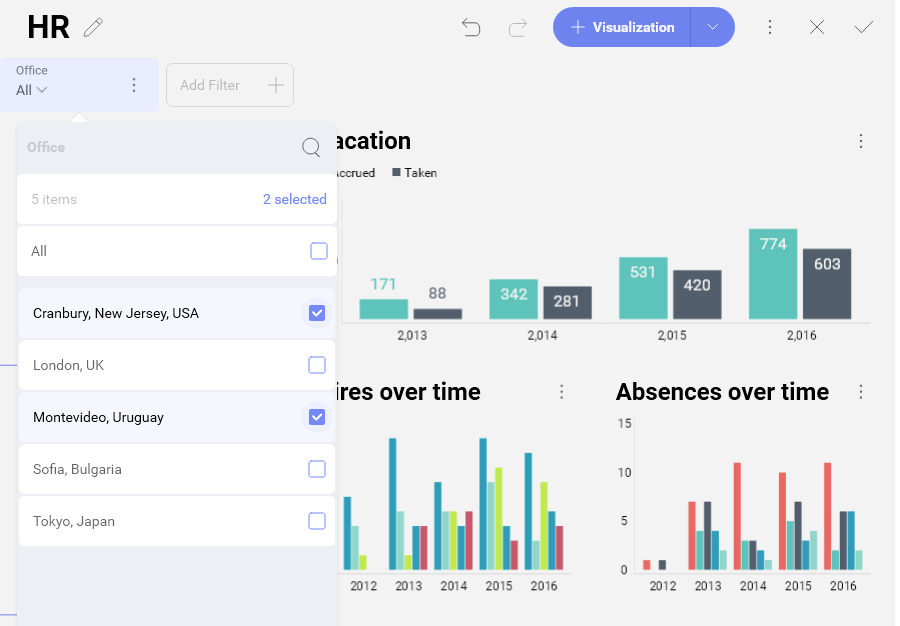
Reveal supports the selection of multiple dashboard filter values simultaneously. This is meant to enable side by side comparison between different elements in a collection. For instance, in the HR Dashboard dashboard you can compare the hires and absences over time of different offices by enabling multiple selection.
In order to enable "Multiple Selection", you must switch the dashboard to Edit mode ⇒ choose Edit from the overflow menu of a dashboard filter ⇒ Selection ⇒ tick Multiple Selection checkbox.
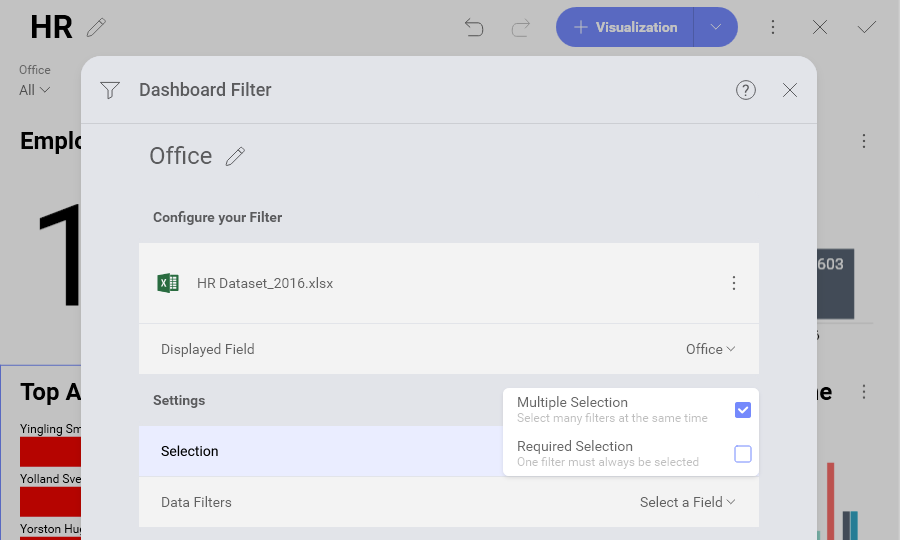
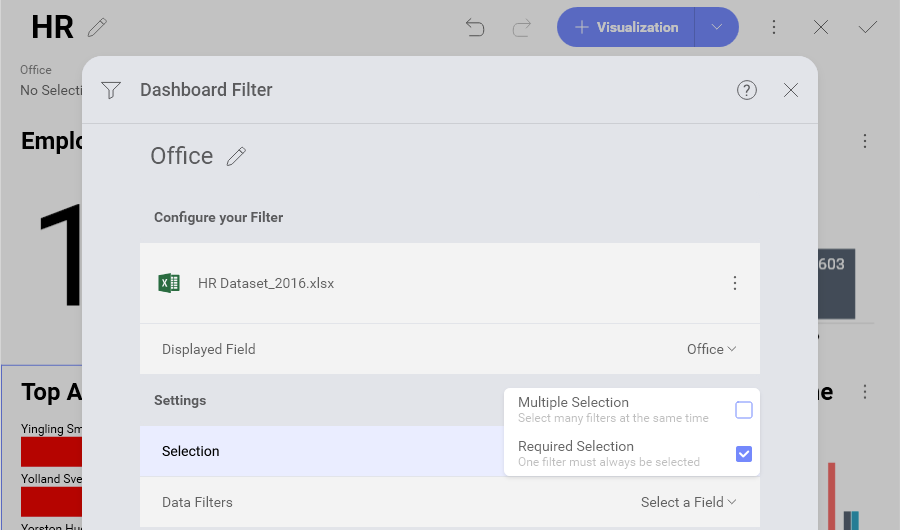
Dashboard filters can be configured to require a selected option or not. By default, selections are not required. Making selections optional allows the user to uncheck all dashboard filter values, which removes the filter from the performed query. The query retrieves all data from the data source, and No Selection is displayed in the dashboard filters row.
In order to enable "Required Selection", you must switch the dashboard to Edit mode ⇒ choose Edit from the overflow menu of a dashboard filter ⇒ Selection ⇒ tick Required Selection checkbox.
You can also apply filters to the fields in the dataset displayed in the Dashboard Filter. This allows you to filter out null or empty values on a specific field (empty values filter). You can also select specific values, or add rules to your field in order to change the options depending on the field type. For more information, visit the field filters and rules section.
For example, if you use the Employee Name field to filter the data in your HR Dashboard, the Dashboard filter will show a list of all employees in all offices of the company:
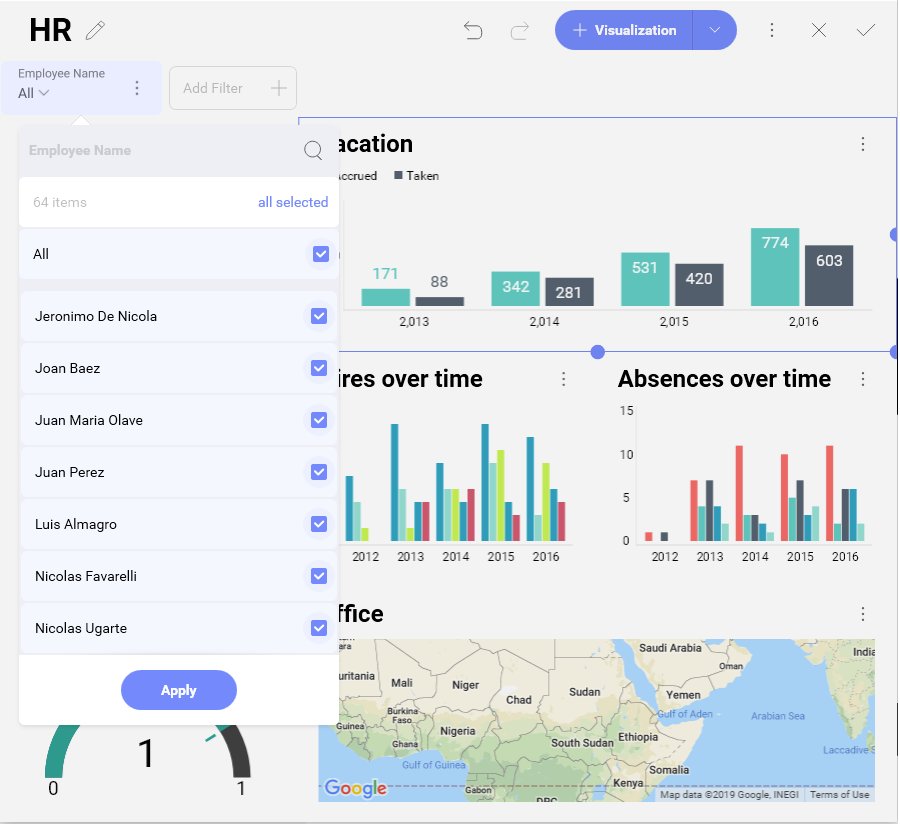
In this case, you can apply the Data Filter property, if you want to use as a filter only employees working in a particular office, e.g. London, UK. This way your dashboard filter will show a list of the employees working in the London office to choose from.
To apply field filters and rules to the data source used as a dashboard filter and have the dashboard filter show only the employees in the London, UK office (as in the example above), follow these steps:
Go to Data Filters in Dashboard Filter settings.
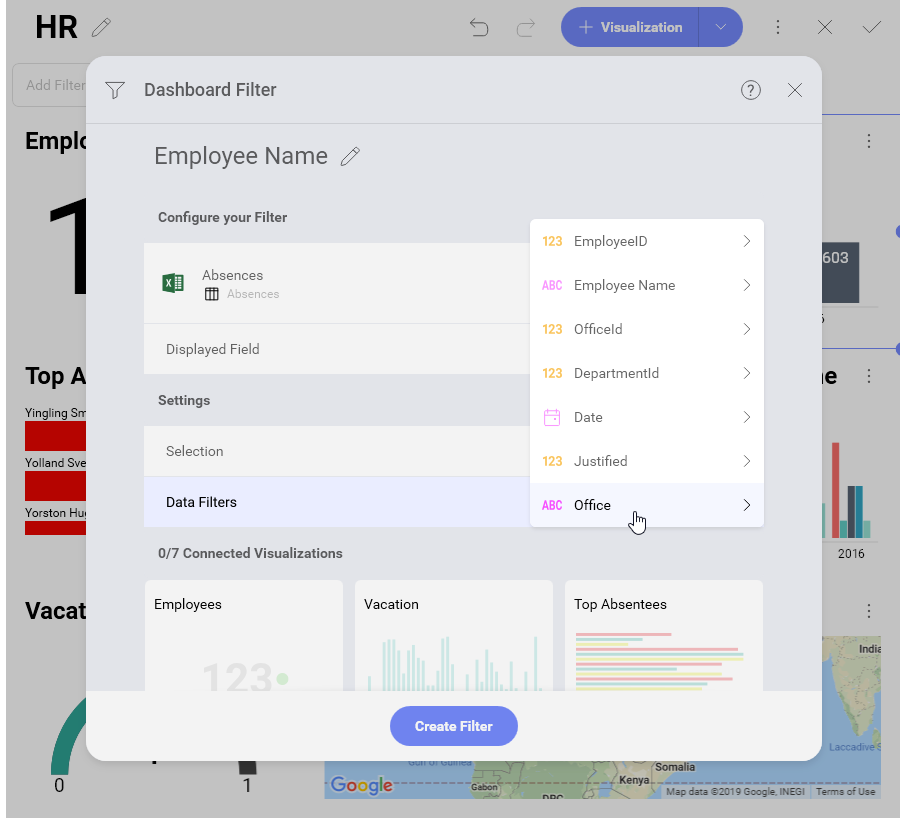
Select Employee name for the Displayed Field property.
Click/tap Select a Field and choose Office from the list.
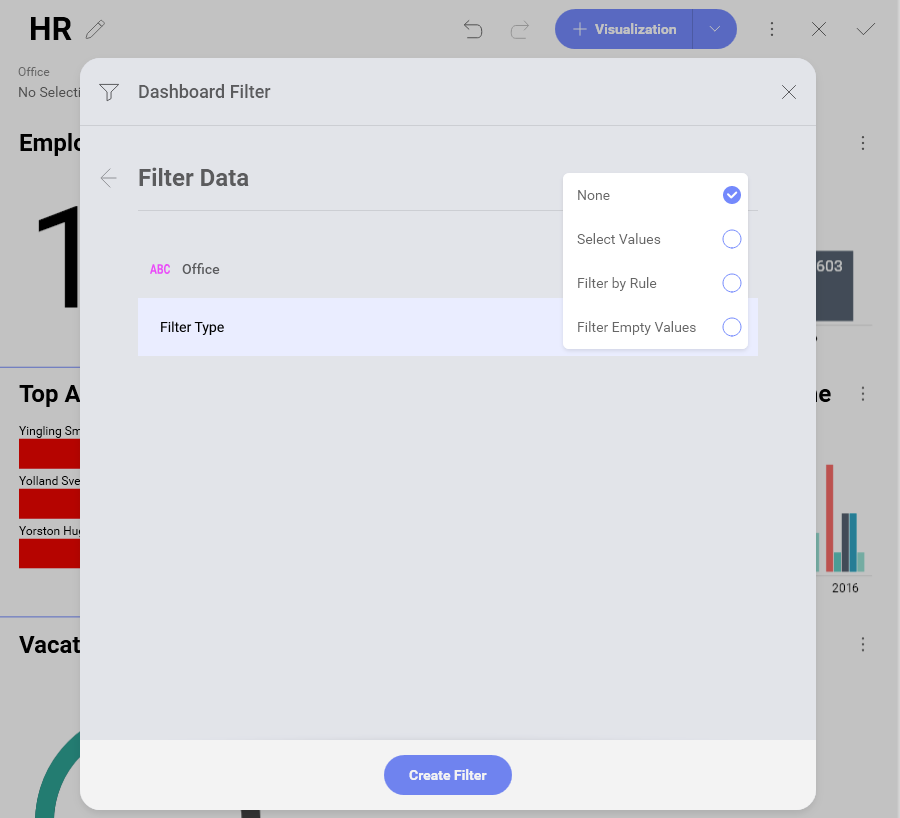
In the following dialog, select the filter type you want to apply (choose Select Values for the purposes of this example):
Choose London, UK from the list and click/tap the Create Filter button.
Now that you have already created your dashboard filter, you will need to connect it to the visualizations you want to apply filtering to. To learn more about this, please read Connecting Dashboard Filters to a Visualization.